Disclaimer For educational purposes only. Do not use as medical advice
AboutChinese MedicineCaution/Notes
| Health Benefits |
| For: |
| Atributes: Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan • Si Jun Zi Tang • Li Zhong Hua Tang Wan • Liu An Jian • Jia Wei Er Chen Tang |
| Constituents: |
| Products (online examples) |
|
|
|
|
|
| Category: Treat Damp Phlegm ⌕ |
| Subcategory: Damp Phlegm Source: Tai Ping Hui Min He Ji Ju Fang |
| Actions: Dries dampness, transforms phlegm, regulates the qi, and harmonizes the middle Jiao [31]
|
| Diagnosis |
| Tongue: white slippery, greasy coating Pulse: Slippery Other: |
| Patterns: Phlegm disturbing the heart, Damp phlegm in Lungs, Phlegm dampness in the Spleen, Damp Phlegm [hiccups] |
| Indications: Damp phlegm in LU and Middle Jiao. [35] • Cough, nausea & vomiting, easy to expectorate white phlegm, white greasy tongue coating, slippery pulse •
Damp-phlegm syndrome (Sp fails to trans., damp accumulation forms phlegm) • Phlegm attacks LU: cough with large amount of white phlegm • ST fails to descend: nausea, vomiting • Phlegm obstruct qi movement: chest and epigastrium oppressed • Phlegm dampness obstructed SP: heaviness • Phlegm blocks clear yang: dizzy • Phlegm disturbs heart: palpitation [31]
|
| Contraindications: |
| Description |
| Name Variations: Er Chen Tang, 二陈汤, Two-Cured Decoction, |
| Herb List: Ban Xia(K, 15g) • Chen Pi(M, 15g) • Fu Ling(A, 9g) • Gan Cao(E, 4.5g) • [Wu Mei(E) • Sheng Jiang(E)] |
| Commentary: "chen" means the longer you keep the herbs, the more potent they are. There are 6 "chen" herbs in the materia medica: Ban Xia, Chen Pi, Ma Huang, Wu Zhu Yu, Zhi Shi, and Long Du(poisonous, no longer used). Xin Hui Chen Pi is the known for being the best quality. Ginger reduces the toxicity of Ban Xia. The basic processed form is Fa Ban Xia to eliminate dampness and phlegm. The most efficient way to get rid of dampness is to promote urination. Fu Ling promotes urination. Some formulas remove Wu Mei because it's sour and from the stabilize and bind category so it's contra to the purpose of the formula. However, some thinks that Wu Mei is used to gather the phlegm and expel it.[Song] • Source text said to add Sheng Jiang and Wu Mei but most modern literature omits it. Modern use also substitute Chen Pi for Ju Hong. [14] |
Related Formulas: Liu Jun Zi Tang, Wen Dan Tang, Bao He Wan, Xing Su San, Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan, Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang
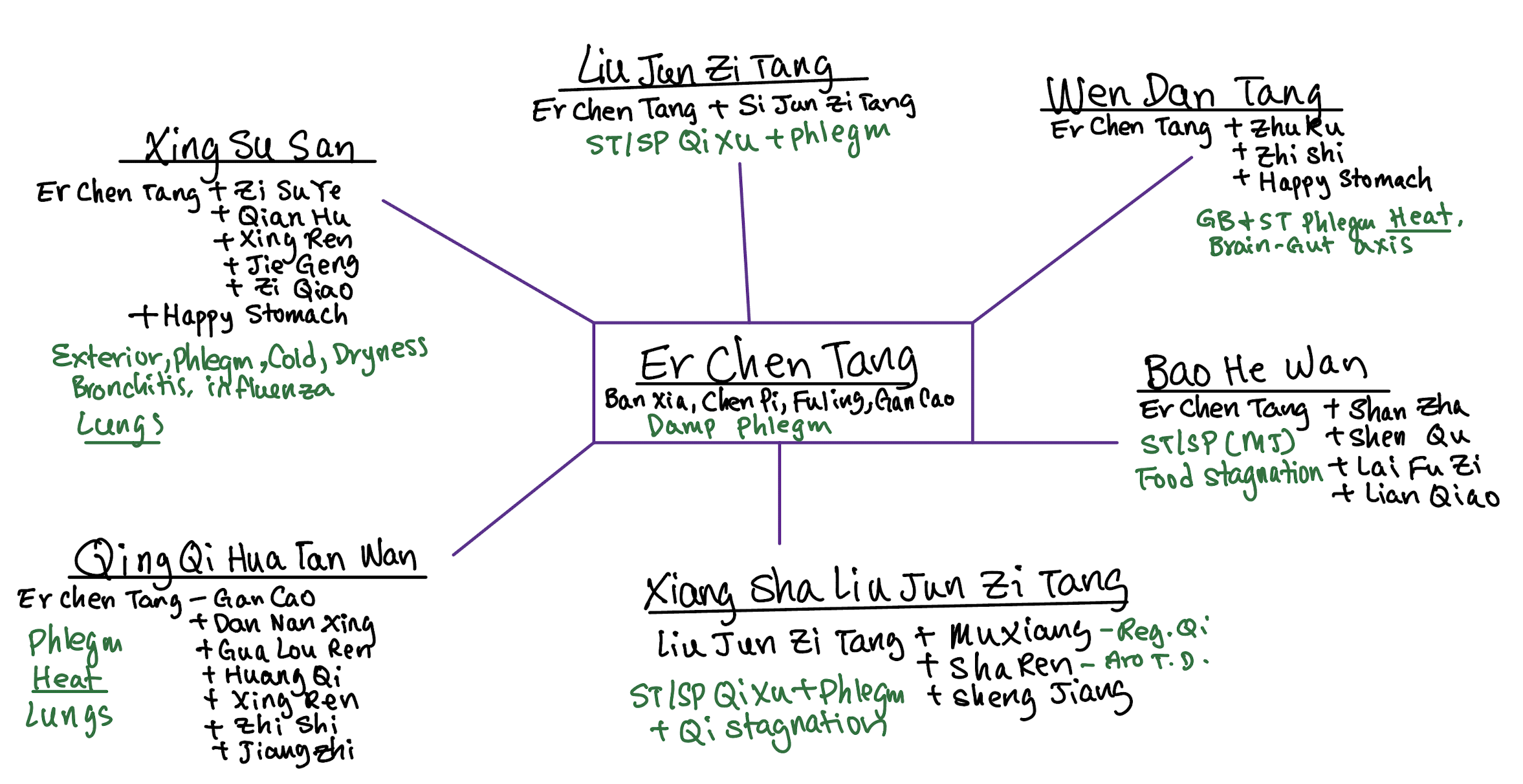 |
| NCCAOM: There are 7 NCCAOM formulas dealing with phlegm. Since it’s phlegm, most of the pulses are slippery. If there’s heat, it’s rapid. 4/7 are for different types of phlegm causing the Lung to cough. The other 3 are for phlegm in different organs. Of the 4 that are for Lung cough: Qīng Qì Huà Tán Wán is Heat Phlegm with viscous sputum. T: red, yellow sticky coat. Herbs: Ban Xia, Chen Pi, Fu Ling, Xing Ren, Zhi Zi, Dan Nan Xing, Gua Lou Ren, Huang Qi. • Bèi Mǔ Guā Lóu Sǎn is for Dry Phlegm with hard to expectorate sputum T: dry white coat. Herbs: Chuan Bei Mu, Gua Lou, Tian Hua Fen, Fu Ling, Ju Hong, Jie Geng • Sān Zi Yǎng Qīn Tāng is for Cold Phlegm + Food/Qi stagnation with profuse sputum. Too much cold/raw food. Good for geriatric/weak patients. T: white greasy coat. Herbs: Bai Jie Zi, Zi Su Zi, Lai Fu Zi. • Zhǐ Sòu Sǎn is for external wind attacking LU causing cough. Cough that won’t go away after a cold or flu. T: thin white coat. P: floating, slow. Herbs: Zi Wan, Bai Bu, Bai Qian, Jie Geng, Chen Pi, Jing Jie, Gan Cao. • The other three are Èr Chén Tāng for Damp phlegm in Middle Jiao causing nausea/vomiting with white easy to expectorate sputum. T: white greasy coat. No heat signs, only damp. Herbs: Ban Xia, Cheng Pi, Fu Ling, Gan Cao. • Wēn Dǎn Tāng is for Heat Phlegm in GB and ST. Profuse sputum. T: white or yellow coat. More for psychiatric issues like insomnia, anxiety, palpitations, brain-gut axis. Herbs: Ban Xia, Cheng Pi, Fu Ling, Zhu Ru, Zhi Shi, Happy Stomach. • Bàn Xià Bái Zhú Tiān Má Tāng is for Internal Wind phlegm (dizziness, vertigo). Copious sputum. T: white greasy. Herbs: Ban Xia, Fu Ling, Tian Ma, Bai Zhu, Ju Hong, Gan Cao. • Qing Qi Hua Tan Wan and Wen Dan Tang includes the main ingredients in Er Chen Tang (Ban Xia, Cheng Pi, Fu Ling). |
| Herbs |
Cat/Dosage |
Actions |
Attributes |
| Zhi Ban Xia • Pinellia Root • 半夏 ♠ |
Phlegm Cold
15g |
Transforms damp-phlegm • Direct stomach Qi downward• Stop cough/ wheezing • Relieve nausea & vomiting • Dissolve nodules and swellingsFan Ban Xia - deep fried with vinegar, Ming Fan, and Sheng Jiang • Jiang Ban Xia - fried with ginger juice |
reprotoxic, warming, drying, antitussive, antiemetic |
| Chen Pi • Dried Tangerine Rind • 陈皮♥ |
Regulate Qi
15g |
Stop cough • Stop vomiting • Regulate Qi • Harmonize middle burner • Transform phlegm • Dry damp • Prevent cloying of tonifying herbs Dao Di: Guang Dong • The older the Chen Pi, the better the quality • For moving Qi, Chen Pi is focus on moving Qi in the epigastric area |
regulate gastrointestinal smooth muscles, clear phlegm, hypertensive, aid digestion, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, expectorant |
| Fu Ling • Poria Mushroom • 茯苓♣ |
Drain Dampness
9g |
Dry dampness • Tonify spleen • Calm spirit • Relief edema • Detox food poisoning • Promote urination Dao Di: Yun Nan |
Diuretic • Antibacterial • Anti-inflammatory • Anti-allergic • Hypoglycemic • Antacid • Sedative • Immunity booster |
| Gan Cao • Licorice Root • 甘草 ♦ |
Tonify Qi
4.5g |
Tonify Spleen Qi • Tonify Heart qi • Clear heat • Resolve toxicity • Stop cough • Dispel phlegm • Lubricate lungs • Stop wheezing • Reduce spasm • Relieve pain • Harmonize other herb effects • enters 12 channelsEnters all 12 channels, often serve as envoy in a formula. |
Hypoglycemic • Antiarrhythmic • Hypertensive • Expectorant • Antidiarrheal • Antiulcer • Hepatoprotective • Immunostimulant • Antitussive • Antiviral • Detox • Demulcent • Anti-inflammatory • Laxative • Emmenagogue • Antimicrobial • Spasmolytic • Corticosteroidal |
| Wu Mei • Mume Fruit • 乌梅 ♦ |
Stabilize + Bind
1 piece |
Inactivate roundworms, stabilize and bind intestines, stop bleeding, prevent Lung Qi leakage |
|
| Sheng Jiang • Ginger (Raw) • 生姜 ♦ |
Release Exterior Wind Cold
7 slices |
Release exterior • Stops vomiting • Relieve Nausea • Stops cough • Reduce herb toxicity • Regulate central flow of Qi |
Expectorant • Cough Suppressant • Digestive • Hypotensive • Antiplatelet • Stimulant • Analgesic • Anti-inflammatory • Antipyretic • Cholagogic • Antiemetic • Antimutagenic |
| ♠ King/Chief ♥ Minister/Deputy ♣ Assistant ♦ Envoy |
| Directions: Original text: take 12g with 7 pieces of Sheng Jiang and 1 piece of Wu Mei. Many modern prescriptions discount this step and substitute Chen pi for Ju Hong. If decoted, the dosage should be reduced by 1/3. |
| Modifications |
For |
| + Cang Zhu + Hou Po |
Damp Phlegm 31 |
| + Dan Nan Xing + Gua Lou |
Heat Phlegm 31 |
| + Gan Jiang + Xi Xin |
Cold Phlegm 31 |
| + Tian Ma + Jiang Can |
Wind Phlegm 31 |
| + Lai Fu Zi + Mai Ya |
Food Stagnation 31 |
| + Xiang Fu + Qing Pi + Yu Jin |
Qi Stagnation 31 |
| + Hai Zao + Kun Bu + Mu Li |
Goiter 31 |
| Caution |
|
ALERT: Contraindications of each herb - use with caution under these conditions:
Ban Xia: Yin deficiency cough • Bleeding • Dehydration • Heat • Pregnancy • Incompatible with Wu Tou and Fu Zi • Antidepressant drugs • Blood pressure medication • Terfenadine (antihistamine) • Foods: lamb, goat
Chen Pi: Excess internal heat • Dry cough from heat, yin deficiency or qi deficiency • Cough with blood • Red tongue • Fluid deficiency
Fu Ling: Foods: Vinegar, pickled food
Gan Cao: High blood pressure • Low potassium • Seaweed • Medications: Gan Cao can interact with various medication. See Pharma Interaction section.
Wu Mei: intestinal excess heat or stagnation, exterior disorder
Sheng Jiang: Lung heat • Dry cough • Phlegm heat • Full heat • Yin deficiency with heat • Vomiting from stomach heat • Gallstones • Exterior deficiency with unexplained sweating • Horse meat |


0 Comments