Disclaimer For educational purposes only. Do not use as medical advice
AboutHerbsCaution/Notes
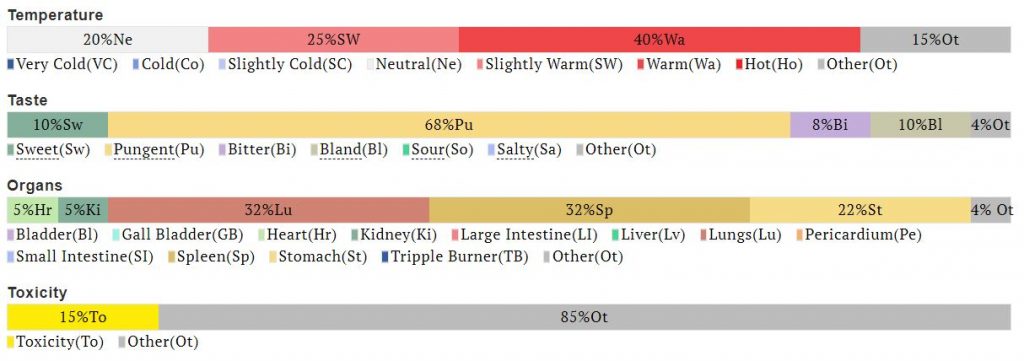
| Health Benefits |
| For: Laryngitis • Tracheitis • Hysteria • Neurosis |
| Attributes: |
| Categories (Click on ⌕ for other formulas in the category) |
| Category: Regulate Qi ⌕ Subcategory: Promote Movement of Qi ⌕ Family: ⌕ Source: Shang Han Lun ⌕ Related Formula: |
| Actions |
| Move Qi • Dissolve clumps • Transform phlegm • Direct rebellious Qi downward |
| Indications and Contraindications |
| Appearance: Tongue -Pink tongue • Greasy, white, thick coat Pulse -Slippery • Slow Face/other - |
| Patterns: |
| Indications: A feeling of throat blockage where it can not be coughed up or swallowed • Stifling sensation in the chest • Vomiting • Melancholy • Depression • Hypochondriac pain |
| Contraindications: Yin Deficiency • Red tongue •Red face • Bitter taste in mouth • Not for long term use |
| Properties |
| Data adapted from product found online. Categories 4% or less not shown. |
 |
| Herbs |
Cat/Dose |
Actions |
Properties |
| Zhi Ban Xia • Pinellia Root • 半夏 ♠ |
Phlegm Cold
9g-12g |
Transforms damp-phlegm • Direct stomach Qi downward• Stop cough/ wheezing • Relieve nausea & vomiting • Dissolve nodules and swellingsFan Ban Xia - deep fried with vinegar, Ming Fan, and Sheng Jiang • Jiang Ban Xia - fried with ginger juice |
reprotoxic, warming, drying, antitussive, antiemetic |
| Hou Po • Magnolia Bark • 厚朴 ♥ |
Aromatic Transform Damp
9g |
Transform spleen dampness • Transform stomach dampness • Clear food stagnation • Transform Phlegm • Clear qi stagnationPairs with Cang Zhu |
GABA-ergic • Sedative • Cannabimimetic • Antioxidant • Anticoagulant • Antidepressant • Anti-inflammatory • Antibiotic • Antispasmodic • Antitumor • Antimicrobial |
| Fu Ling • Poria Mushroom • 茯苓 ♥ |
Drain Dampness
12g |
Dry dampness • Tonify spleen • Calm spirit • Relief edema • Detox food poisoning • Promote urination Dao Di: Yun Nan |
Diuretic • Antibacterial • Anti-inflammatory • Anti-allergic • Hypoglycemic • Antacid • Sedative • Immunity booster |
| Sheng Jiang • Ginger (Raw) • 生姜 ♣ |
Release Exterior Wind Cold
9g |
Release exterior • Stops vomiting • Relieve Nausea • Stops cough • Reduce herb toxicity • Regulate central flow of Qi |
Expectorant • Cough Suppressant • Digestive • Hypotensive • Antiplatelet • Stimulant • Analgesic • Anti-inflammatory • Antipyretic • Cholagogic • Antiemetic • Antimutagenic |
| Zi Su Ye • Perilla Leaf • 紫苏叶 ♦ |
Release Exterior Wind Cold
6g |
Release the exterior • Expel cold • Calm restless fetus and morning sickness • Detox seafood poisoning • Harmonize the middle burner • Move qi • Harmonize spleen • Induce sweating • Revives spleen • 15g for parasitesPerilla stem and leaf are combined to bear down on qi and disperse phlegm • Use the purple leaves, not green. |
antiparasitic, anti-inflammation, antipyretic, bronchio dilator, hypoglycemic, antitussive, antibacterial, diaphoretic, GI tract stimulator |
| ♠ King/Chief ♥ Minister/Deputy ♣ Assistant ♦ Envoy |
| Directions: |
| Modifications |
For |
| +Xie Bai + Gua Lou |
Chest pain |
| + Jin Ling Zi + Yan Hu Suo |
Hypochondriac Pain |
| + Jie Geng + Xuan Shen |
Painful throat swelling |
| + Yu Jin + Chai Hu +Xiang Fu + Qing Pi |
Highly stagnant Qi |
| + Ding Xiang + Bai Dou Kou +Sha Ren |
Vomiting |
| + Mu Xiang + Sha Ren |
Abdominal distention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Caution |
ALERT: Contraindications of each herb - use with caution under these conditions:
Ban Xia: Yin deficiency cough • Bleeding • Dehydration • Heat • Pregnancy • Incompatible with Wu Tou and Fu Zi • Antidepressant drugs • Blood pressure medication • Terfenadine (antihistamine) • Foods: lamb, goat
Hou Po: Anticoagulant drugs • Antidepressant drugs
Fu Ling: Foods: Vinegar, pickled food
Sheng Jiang: Lung heat • Dry cough • Phlegm heat • Full heat • Yin deficiency with heat • Vomiting from stomach heat • Gallstones • Exterior deficiency with unexplained sweating • Horse meat
Zi Su Ye: Warm Pathogen Diseases • Qi-Deficiency • Exterior Deficiencies • Damp Heat • Spontaneous Sweating |




0 Comments